KS4 Tree of life
Challenge overview
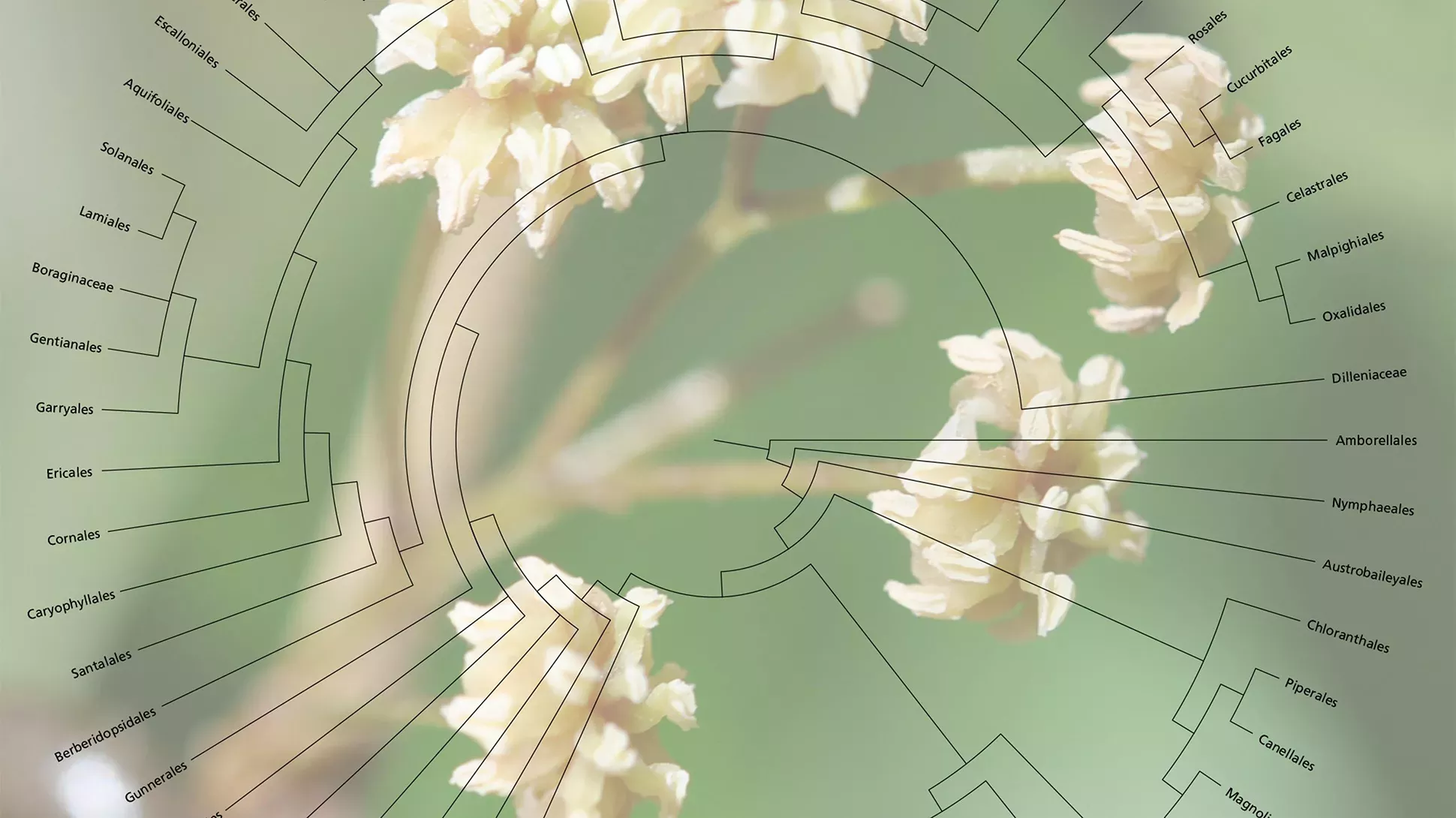
Pupils will construct an evolutionary tree using their own classification system for the plants in your school grounds or nearby park/green space, then compare with data from Kew’s Plant and Fungal Trees of Life (PAFTOL).
Learning outcomes
-
Understand the importance and applications of Kew’s Plant and Fungal Trees of Life project
-
Understand how the analysis of DNA sequence data has helped inform the modern classification system
-
Understand that evidence for the modern theory of evolution by natural selection includes DNA sequence data
-
Apply knowledge of sampling techniques to ensure a representative sample
Key vocabulary
Classification, genetics, genome, DNA, evolutionary tree, fieldwork, sampling, methodology
Background information
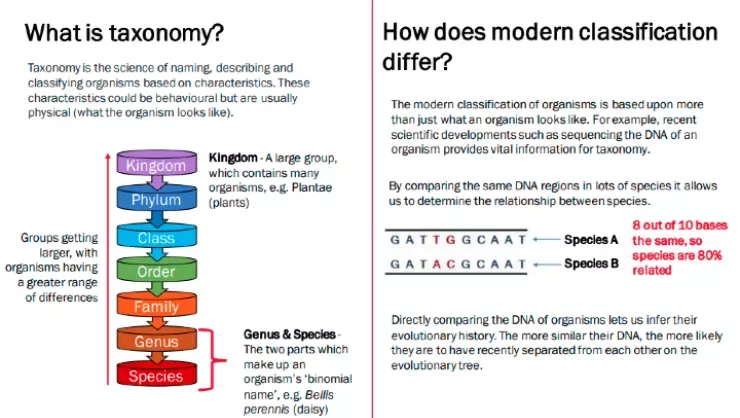
How are the world’s plants and fungi related to each other and how have they evolved over time? Linnaeus’s original system of classification grouped organisms by physical characteristic – whether they looked similar or different. Since then, advances in technology mean that we can now classify plants by their DNA sequences.
Find out how Kew’s Plant and Fungal Trees of Life (PAFTOL) project is using DNA sequencing technology to complete the evolutionary tree of life.
Did you know?
Kew’s Plant and Fungal Trees of Life project aims to generate DNA sequence data for at least one species from each of the approximately 14,000 flowering plant and 8,200 fungal genera.

Wow fact
PAFTOL scientists have sequenced hundreds of genes from herbarium samples that are over 200 years old!
Curriculum links
4.6 Inheritance, variation and evolution
4.6.1.4 DNA and the genome
- The genome of an organism is the entire genetic material of that organism
4.6.2.2 Evolution
- The theory of evolution by natural selection states that all species of living things have evolved from simple life forms that first developed more than three billion years ago
- If two populations of one species become so different in phenotype that they can no longer interbreed to produce fertile offspring they have formed two new species
4.6.3.4 Evidence for evolution
- Evidence for Darwin’s theory is now available as it has been shown that characteristics are passed on to offspring in genes. There is further evidence in the fossil record
4.6.3.5 Fossils
- We can learn from fossils how much or how little different organisms have changed as life developed on Earth
- Students should be able to extract and interpret information from charts, graphs and tables such as evolutionary trees
4.6.4 Classification of living organisms
- Traditionally living things have been classified into groups depending on their structure and characteristics in a system developed by Carl Linnaeus
- Linnaeus classified living things into kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus and species. Organisms are named by the binomial system of genus and species
- Students should be able to describe the impact of developments in biology on classification systems
- Evolutionary trees are a method used by scientists to show how they believe organisms are related. They use current classification data for living organisms and fossil data for extinct organisms
Working scientifically
- Understand how scientific methods and theories develop over time
- Appreciate the power and limitations of science and consider any ethical issues which may arise
- Explain everyday and technological applications of science; evaluate associated personal, social, economic and environmental implications; and make decisions based on the evaluation of evidence and arguments
- Recognise the importance of peer review of results and of communicating results to a range of audiences
Experimental skills and strategies
- Recognise when to apply a knowledge of sampling techniques to ensure any samples collected are representative
- Communicating the scientific rationale for investigations, methods used, findings and reasoned conclusions through paper-based and electronic reports and presentations using verbal, diagrammatic, graphical, numerical and symbolic forms
8.2.9 Required practical activity 9
- Measure the population size of a common species in a habitat
Topic 3 – Genetics
- Describe the genome as the entire DNA of an organism and a gene as a section of a DNA molecule that codes for a specific protein
- Explain how DNA can be extracted from fruit
Topic 4 – Natural selection and genetic modification
- Explain Darwin’s theory of evolution by natural selection
- Describe how genetic analysis has led to the suggestion of the three domains rather than the five kingdoms classification method
Topic 9 – Ecosystems and material cycles
Core practical 9.5
- Investigate the relationship between organisms and their environment using field-work techniques, including quadrats and belt transects
Working scientifically
- Understand how scientific methods and theories develop over time
- Appreciate the power and limitations of science and consider any ethical issues which may arise
- Explain everyday and technological applications of science; evaluate associated personal, social, economic and environmental implications; and make decisions based on the evaluation of evidence and arguments
- Recognise the importance of peer review of results and of communicating results to a range of audiences
Experimental skills and strategies
- Recognise when to apply a knowledge of sampling techniques to ensure any samples collected are representative
- Communicating the scientific rationale for investigations, methods used, findings and reasoned conclusions through paper-based and electronic reports and presentations using verbal, diagrammatic, graphical, numerical and symbolic forms
Topic B5: Genes, inheritance and selection
B5.1 Inheritance
- Describe the genome as the entire genetic material of an organism
B5.2 Natural selection and evolution
- Describe the impact of developments in biology on classification systems. To include: natural and artificial classification systems and use of molecular phylogenetics based on DNA sequencing
- Describe evolution as a change in the inherited characteristics of a population over time, through a process of natural selection, which may result in the formation of new species
- Describe the evidence for evolution. To include: fossils
- Describe the work of Darwin and Wallace in the development of the theory of evolution by natural selection and explain the impact of these ideas on modern biology
Working scientifically
- Understand how scientific methods and theories develop over time
- Appreciate the power and limitations of science and consider any ethical issues which may arise
- Explain everyday and technological applications of science; evaluate associated personal, social, economic and environmental implications; and make decisions based on the evaluation of evidence and arguments
- Recognise the importance of peer review of results and of communicating results to a range of audiences
Experimental skills and strategies
- Recognise when to apply a knowledge of sampling techniques to ensure any samples collected are representative
- Communicating the scientific rationale for investigations, methods used, findings and reasoned conclusions through paper-based and electronic reports and presentations using verbal, diagrammatic, graphical, numerical and symbolic forms
Chapter B1: You and your genes
B1.1 What is the genome and what does it do?
- All the genetic material of a cell is the organism’s genome
Chapter B3: Living together – food and ecosystems
B3.4 How are populations affected by conditions in an ecosystem?
- The distribution and abundance of organisms, and changing conditions, within an ecosystem can be investigated using techniques including: identification keys; transects and quadrats
- Investigate the distribution and abundance of organisms in an ecosystem
Chapter B6: Life on Earth – past, present and future
B6.1 How was the theory of evolution developed?
- The modern theory of evolution by natural selection combines ideas about genes, variation, advantage and competition to explain how the inherited characteristics of a population can change over a number of generations
- A new species can arise if the organisms in a population evolve to be so different from their ancestors that they could no longer mate with them to produce fertile offspring
- The theory of evolution by natural selection was developed to explain observations made by Darwin, Wallace and other scientists, including:
- the production of new varieties of plants and animals by selective breeding
- fossils with similarities and differences to living species
- the different characteristics shown by isolated populations of the same species living in different ecosystems
- The theory of evolution by natural selection illustrates how scientists continue to test a proposed explanation by making new observations and collecting new evidence, and how if the explanation is able to explain these it can become widely accepted by the scientific community
B6.3 How does our understanding of biology help us classify the diversity of organisms on Earth?
- The enormous diversity of organisms on Earth can be classified into groups on the basis of observed similarities and differences in their physical characteristics and, more recently, their DNA. We are more likely to classify species into the same group if there are lots of similarities in their genomes (i.e. if they have many genes, and genetic variants, in common). Genome analysis can also suggest whether different groups have a common ancestor, and how recently speciation occurred
- Describe the impact of developments in biology on classification systems, including the use of DNA analysis to classify organisms
Chapter B7: Ideas about Science
IaS1 What needs to be considered when investigating a phenomenon scientifically?
- The aim of science is to develop good explanations for natural phenomena. There is no single ‘scientific method’ that leads to good explanations, but scientists do have characteristic ways of working. In particular, scientific explanations are based on a cycle of collecting and analysing data
IaS3 How are scientific explanations developed?
- Scientific explanations and theories do not ‘emerge’ automatically from data, and are separate from the data. Proposing an explanation involves creative thinking. Collecting sufficient data from which to develop an explanation often relies on technological developments that enable new observations to be made
- Findings reported by an individual scientist or group are carefully checked by the scientific community before being accepted as scientific knowledge
IaS4 How do science and technology impact society?
- Scientists must communicate their work to a range of audiences, including the public, other scientists, and politicians, in ways that can be understood. This enables decision-making based on information about risks, benefits, costs and ethical issues
Chapter B8: Practical skill
- Application of appropriate sampling techniques to investigate the distribution and abundance of organisms in an ecosystem via direct use in the field
How to run the challenge
Part 1: Challenge preparation (1 hour)
We recommend this is completed in class with the teacher.
-
Introduce the challenge to your class by playing the short clip in the overview. All the other tools needed for the challenge are in the 'Resources' section below
-
Play the Watch and learn video with your class
-
Print out the Odd One Out activity for your pupils to complete in groups, or display the cards on the whiteboard for a whole class approach
-
Print out the Taxonomic Categories resource for your pupils to read, or display the resource on the whiteboard for a whole class approach
-
Print out the supporting resources (“Indicator species guide” and “Sampling strategies”) for your pupils to use during the challenge
-
Print out the ‘From DNA sequences to trees’ resource for pupils to use after they’ve created their own tree
-
Assess your pupil's learning with the quiz
Part 2: The challenge (2-3 hours)
Pupils can complete the challenge alone or in groups, and either in class or as a homework activity.
Kew’s Endeavour challenges are open-ended to encourage pupils to design and carry out their own investigations. For KS4 Tree of life, pupils must construct an evolutionary tree using their own classification system for the plants in your school grounds or nearby park/green space, then compare with the PAFTOL data.
Pupils will need to:
-
design a method for sampling an area
-
look for the indicator species provided
-
photograph or draw the species
-
decide on a system of classification based on physical characteristics:
-
what do the plants look like?
-
can they be grouped by similarities and differences in appearance?
-
-
construct an evolutionary tree for these plants using their classification system
-
use the PAFTOL project’s Tree of Life to find out how closely the plants are related using gene sequence data and construct a new tree based on their DNA
-
compare their two trees; how similar or different are they?
-
write up their findings along with their ideas on why this work is important – why would we need to know how different plants are related to each other?
Resources
KS4 Tree of life watch and learn
Introduce your pupils to gene sequencing technology and evolutionary trees with this

KS4 Tree of life odd one out
Invite your pupils to discover which plants are related to each other.

KS4 Tree of life taxonomic categories
Invite your pupils to explore the science of naming, describing and classifying organisms
KS4 Tree of life indicator species guide
Help your pupils to complete a survey to find the indicator species with this

KS4 Tree of life sampling strategies guide
Find out about different field studies sampling strategies and methods.

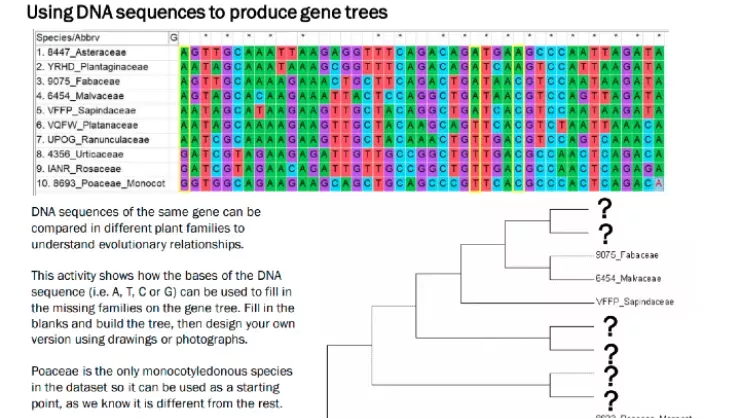
KS4 Tree of life from DNA sequences to trees
Find out how DNA sequence data is used to construct evolutionary trees.
KS4 Tree of life quiz
Test your pupils' knowledge of plant health with this quiz.

Career skills
Endeavour promotes the acquisition of Science Capital, helping your pupils to have a better understanding of science and its relevance in their lives. By taking this challenge your pupils will be using the skills of a bioinformatician.
What does a bioinformatician do?
There are many different jobs that a bioinformatician can perform. One of the jobs of a bioinformatician on the PAFTOL team is to develop and use computer programmes so that DNA sequence data can be assembled into evolutionary trees and analysed.
To do this, a bioinformatician analyses DNA sequences isolated from plant specimens by first aligning them to each other. The pattern of differences in the DNA base residues between each sequence are assessed by specially designed algorithms.
The output is visualized in the form of a tree showing the relationships between the sequences and therefore the plant species themselves (i.e. it is similar to a family tree of human relatives). These evolutionary trees help scientists to interpret the similarities and differences between related species with interesting characteristics.
Skills:
-
Observation - looking at things carefully
-
Attentiveness - able to pay attention to detail
-
Researching - finding relevant information
-
Logic – basing thoughts on facts and evidence and using reasoning to solve problems
-
Classifying - arranging, ordering and grouping things
-
Questioning - identifying areas that can be studied or tested
-
Inferring - making informed judgements
-
Communication - written and verbal
Useful links
Looking for another challenge to do with your class?
KS4 Plant diseases

KS4 Zero hunger

KS4 Kew scientist
